cytoscape-fcose
================================================================================
## Description
fCoSE (pron. "f-cosay", **f**ast **Co**mpound **S**pring **E**mbedder), is a faster version of our earlier compound spring embedder algorithm named [CoSE](https://github.com/cytoscape/cytoscape.js-cose-bilkent), implemented as a Cytoscape.js extension by [i-Vis Lab](http://cs.bilkent.edu.tr/~ivis/) in Bilkent University.
Here are some demos: **simple**, **compound**, and **constraints**, respectively:



fCoSE layout algorithm combines the speed of spectral layout with the aesthetics of force-directed layout. fCoSE runs up to 2 times as fast as CoSE while achieving similar aesthetics.
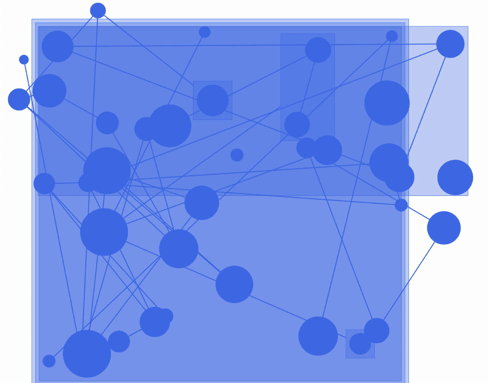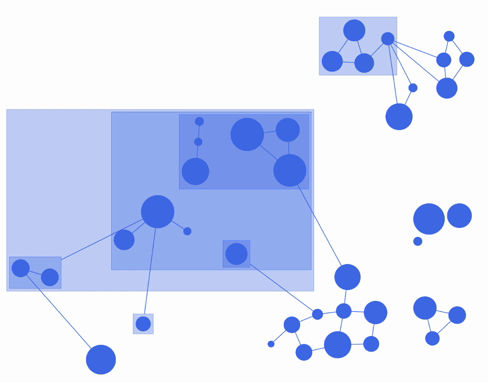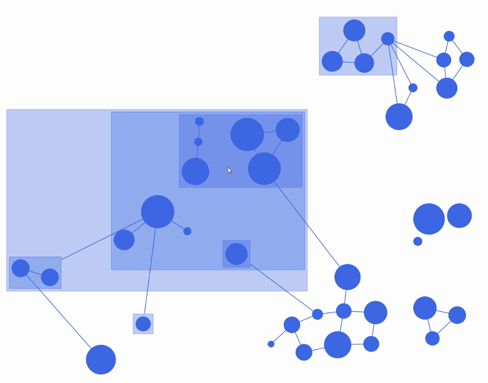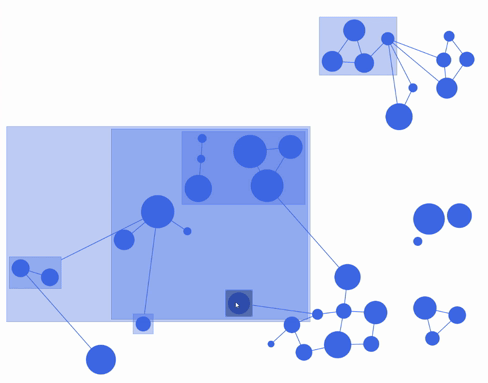
Furthermore, fCoSE also supports a fairly rich set of constraint types (i.e., fixed position, vertical/horizontal alignment and relative placement).
You can see constraint support in action in the following videos: [fixed node](https://youtu.be/vRZVlwntzGY), [alignment](https://youtu.be/O5rddJ7DteU), [relative placement](https://youtu.be/Xcm87bT50RA), [hybrid](https://youtu.be/KRAQHmnTvUA), [real life graphs](https://youtu.be/vTPy9G2ALcI). Constraints can also be added [incrementally](https://youtu.be/DTm2WmzwP4k) on a given layout.
Please cite the following when you use this layout:
H. Balci and U. Dogrusoz, "[fCoSE: A Fast Compound Graph Layout Algorithm with Constraint Support](https://doi.org/10.1109/TVCG.2021.3095303)," in IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 28(12), pp. 4582-4593, 2022.
U. Dogrusoz, E. Giral, A. Cetintas, A. Civril and E. Demir, "[A Layout Algorithm For Undirected Compound Graphs](http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0020025508004799)", Information Sciences, 179, pp. 980-994, 2009.
## Dependencies
* Cytoscape.js ^3.2.0
* cose-base ^2.0.0
* cytoscape-layout-utilities.js (optional for packing disconnected components) ^1.0.0
## Documentation
fCoSE supports user-defined placement constraints as well as its full support for compound graphs. These constraints may be defined for simple nodes. Supported constraint types are:
* **Fixed node constraint:** The user may provide *exact* desired positions for a set of nodes called *fixed nodes*. For example, in order to position node *n1* to *(x: 100, y: 200)* and node *n2* to *(x: 200, y: -300)* as a result of the layout, ```fixedNodeConstraint``` option should be set as follows:
```js
fixedNodeConstraint: [{nodeId: 'n1', position: {x: 100, y: 200}},
{nodeId: 'n2', position: {x: 200, y: -300}}],
```
* **Alignment constraint:** This constraint aims to align two or more nodes (with respect to their centers) vertically or horizontally. For example, for the vertical alignment of nodes {*n1, n2, n3*} and {*n4, n5*}, and horizontal alignment of nodes {*n2, n4*} as a result of the layout, ```alignmentConstraint``` option should be set as follows:
```js
alignmentConstraint: {vertical: [['n1', 'n2', 'n3'], ['n4', 'n5']], horizontal: [['n2', 'n4']]},
```
***Note:** Alignment constraints in a direction must be given in most compact form. Example: ```['n1', 'n2', 'n3']``` instead of ```['n1', 'n2'], ['n1', 'n3']```.*
* **Relative placement constraint:** The user may constrain the position of a node relative to another node in either vertical or horizontal direction. For example, in order to position node *n1* to be above of node *n2* by at least 100 pixels and position node *n3* to be on the left of node *n4* by at least 75 pixels as a result of the layout, ```relativePlacementConstraint``` option should be set as follows:
```js
relativePlacementConstraint: [{top: 'n1', bottom: 'n2', gap: 100},
{left: 'n3', right: 'n4', gap: 75}],
```
The `gap` property is optional. If it is omitted, average `idealEdgeLength` is used as the gap value.
## Usage instructions
Download the library:
* via npm: `npm install cytoscape-fcose`,
* via bower: `bower install cytoscape-fcose`, or
* via direct download in the repository (probably from a tag).
Import the library as appropriate for your project:
ES import:
```js
import cytoscape from 'cytoscape';
import fcose from 'cytoscape-fcose';
cytoscape.use( fcose );
```
CommonJS require:
```js
let cytoscape = require('cytoscape');
let fcose = require('cytoscape-fcose');
cytoscape.use( fcose ); // register extension
```
AMD:
```js
require(['cytoscape', 'cytoscape-fcose'], function( cytoscape, fcose ){
fcose( cytoscape ); // register extension
});
```
Plain HTML/JS has the extension registered for you automatically, because no `require()` is needed. Just add the following files:
```
```
## API
When calling the layout, e.g. `cy.layout({ name: 'fcose', ... })`, the following options are supported:
```js
var defaultOptions = {
// 'draft', 'default' or 'proof'
// - "draft" only applies spectral layout
// - "default" improves the quality with incremental layout (fast cooling rate)
// - "proof" improves the quality with incremental layout (slow cooling rate)
quality: "default",
// Use random node positions at beginning of layout
// if this is set to false, then quality option must be "proof"
randomize: true,
// Whether or not to animate the layout
animate: true,
// Duration of animation in ms, if enabled
animationDuration: 1000,
// Easing of animation, if enabled
animationEasing: undefined,
// Fit the viewport to the repositioned nodes
fit: true,
// Padding around layout
padding: 30,
// Whether to include labels in node dimensions. Valid in "proof" quality
nodeDimensionsIncludeLabels: false,
// Whether or not simple nodes (non-compound nodes) are of uniform dimensions
uniformNodeDimensions: false,
// Whether to pack disconnected components - cytoscape-layout-utilities extension should be registered and initialized
packComponents: true,
// Layout step - all, transformed, enforced, cose - for debug purpose only
step: "all",
/* spectral layout options */
// False for random, true for greedy sampling
samplingType: true,
// Sample size to construct distance matrix
sampleSize: 25,
// Separation amount between nodes
nodeSeparation: 75,
// Power iteration tolerance
piTol: 0.0000001,
/* incremental layout options */
// Node repulsion (non overlapping) multiplier
nodeRepulsion: node => 4500,
// Ideal edge (non nested) length
idealEdgeLength: edge => 50,
// Divisor to compute edge forces
edgeElasticity: edge => 0.45,
// Nesting factor (multiplier) to compute ideal edge length for nested edges
nestingFactor: 0.1,
// Maximum number of iterations to perform - this is a suggested value and might be adjusted by the algorithm as required
numIter: 2500,
// For enabling tiling
tile: true,
// The comparison function to be used while sorting nodes during tiling operation.
// Takes the ids of 2 nodes that will be compared as a parameter and the default tiling operation is performed when this option is not set.
// It works similar to ``compareFunction`` parameter of ``Array.prototype.sort()``
// If node1 is less then node2 by some ordering criterion ``tilingCompareBy(nodeId1, nodeId2)`` must return a negative value
// If node1 is greater then node2 by some ordering criterion ``tilingCompareBy(nodeId1, nodeId2)`` must return a positive value
// If node1 is equal to node2 by some ordering criterion ``tilingCompareBy(nodeId1, nodeId2)`` must return 0
tilingCompareBy: undefined,
// Represents the amount of the vertical space to put between the zero degree members during the tiling operation(can also be a function)
tilingPaddingVertical: 10,
// Represents the amount of the horizontal space to put between the zero degree members during the tiling operation(can also be a function)
tilingPaddingHorizontal: 10,
// Gravity force (constant)
gravity: 0.25,
// Gravity range (constant) for compounds
gravityRangeCompound: 1.5,
// Gravity force (constant) for compounds
gravityCompound: 1.0,
// Gravity range (constant)
gravityRange: 3.8,
// Initial cooling factor for incremental layout
initialEnergyOnIncremental: 0.3,
/* constraint options */
// Fix desired nodes to predefined positions
// [{nodeId: 'n1', position: {x: 100, y: 200}}, {...}]
fixedNodeConstraint: undefined,
// Align desired nodes in vertical/horizontal direction
// {vertical: [['n1', 'n2'], [...]], horizontal: [['n2', 'n4'], [...]]}
alignmentConstraint: undefined,
// Place two nodes relatively in vertical/horizontal direction
// [{top: 'n1', bottom: 'n2', gap: 100}, {left: 'n3', right: 'n4', gap: 75}, {...}]
relativePlacementConstraint: undefined,
/* layout event callbacks */
ready: () => {}, // on layoutready
stop: () => {} // on layoutstop
};
```
To be able to use `packComponents` option, `cytoscape-layout-utilities` extension should also be registered in the application.
Packing related [options](https://github.com/iVis-at-Bilkent/cytoscape.js-layout-utilities#default-options) should be set via `cytoscape-layout-utilities` extension.
If they are not set, fCoSE uses default options.
## Build targets
* `npm run test` : Run Mocha tests in `./test`
* `npm run build` : Build `./src/**` into `cytoscape-fcose.js`
* `npm run watch` : Automatically build on changes with live reloading (N.b. you must already have an HTTP server running)
* `npm run dev` : Automatically build on changes with live reloading with webpack dev server
* `npm run lint` : Run eslint on the source
N.b. all builds use babel, so modern ES features can be used in the `src`.
## Publishing instructions
This project is set up to automatically be published to npm and bower. To publish:
1. Build the extension : `npm run build:release`
1. Commit the build : `git commit -am "Build for release"`
1. Bump the version number and tag: `npm version major|minor|patch`
1. Push to origin: `git push && git push --tags`
1. Publish to npm: `npm publish .`
1. If publishing to bower for the first time, you'll need to run `bower register cytoscape-fcose https://github.com/iVis-at-Bilkent/cytoscape.js-fcose.git`
1. [Make a new release](https://github.com/iVis-at-Bilkent/cytoscape.js-fcose/releases/new) for Zenodo.
## Team
* [Hasan Balcı](https://github.com/hasanbalci) and [Ugur Dogrusoz](https://github.com/ugurdogrusoz) of [i-Vis at Bilkent University](http://www.cs.bilkent.edu.tr/~ivis)




